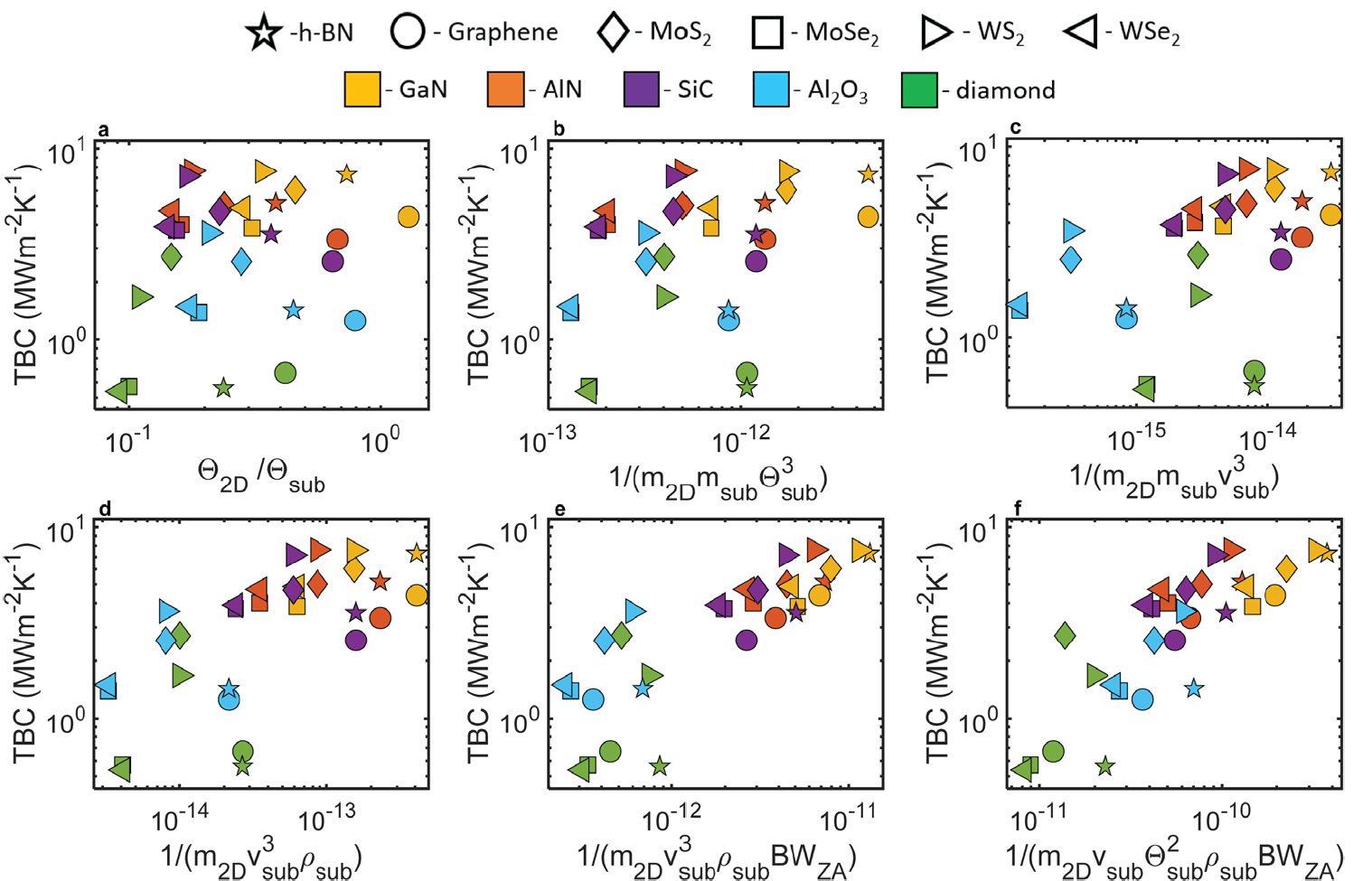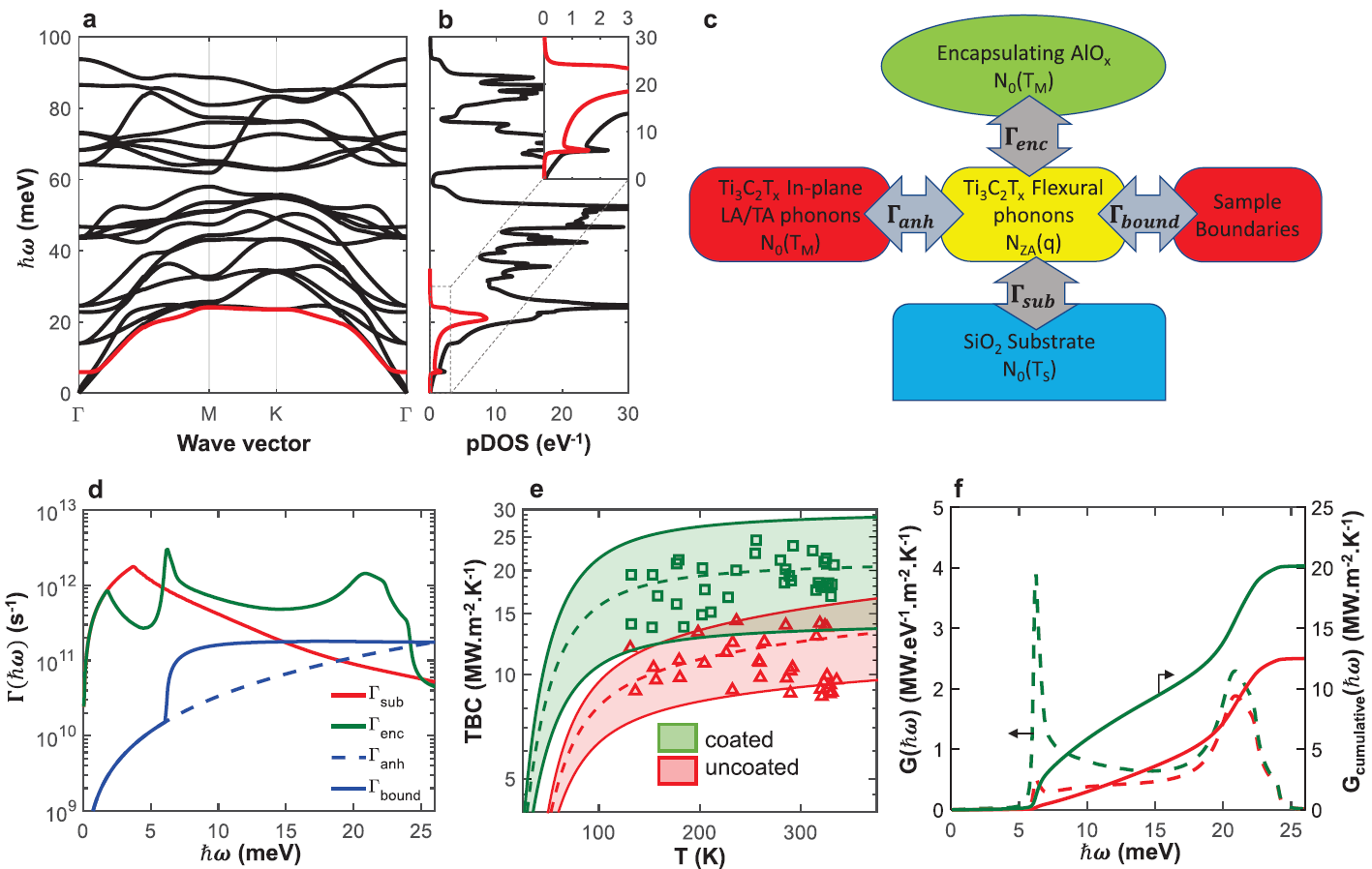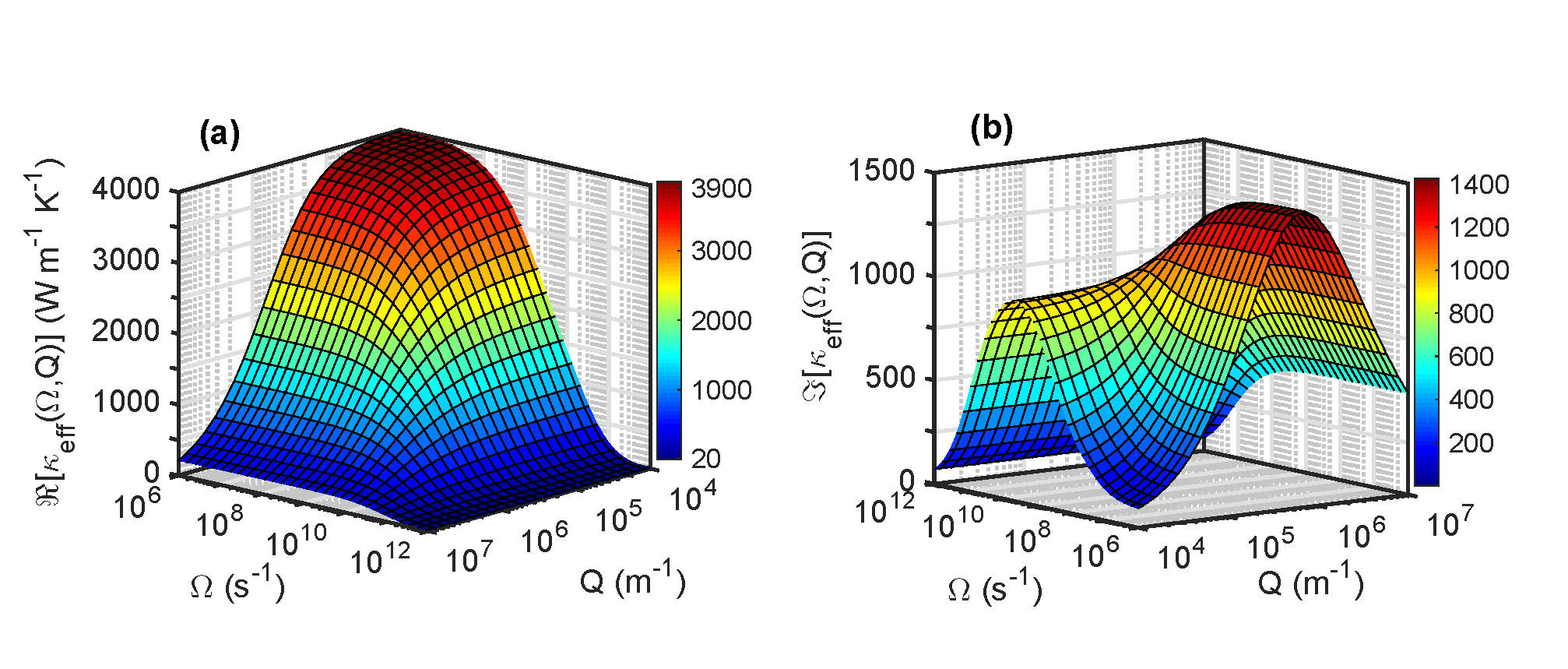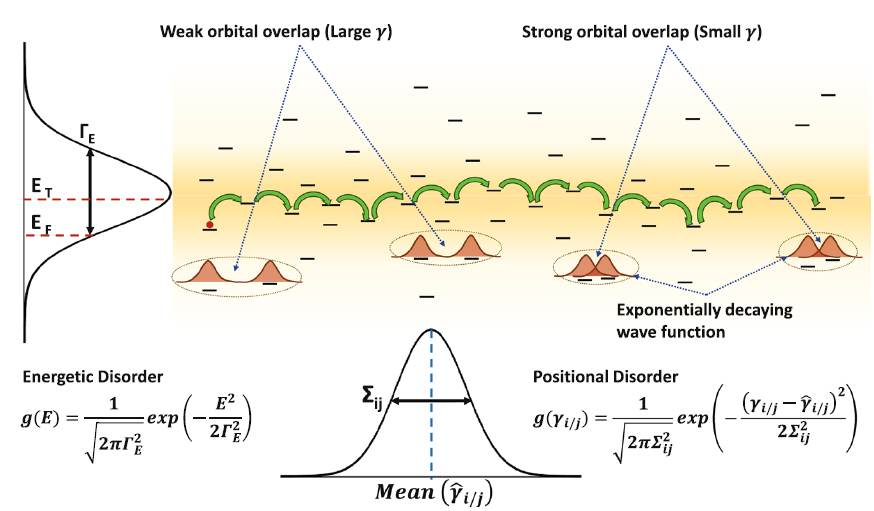
Meenakshi’s work, in collaboration with Prof. Venkataraman’s ALIEN group in UMass Chemistry, studies how to leverage disorder in amorphous organic materials such as polymers to improve their thermoelectric performance. The paper is open access and free to read via Scientific Reports: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42265-z